What is Synovitis?
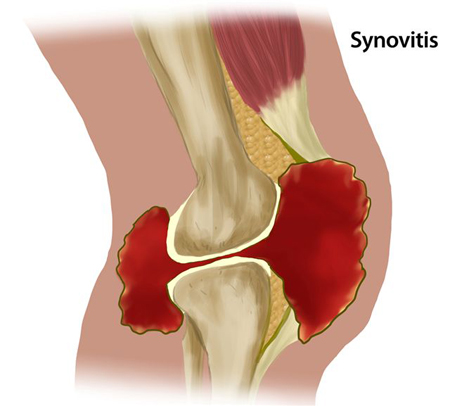
The synovial membrane is the part of the body that lines the inside of certain joints. It lines the joint capsule in the knee, ankle, wrist, elbow, hand, foot, and shoulder. When this membrane gets inflamed, it is called synovitis. Synovitis is often the result of repeated joint bleeds that are not treated early or correctly. With synovitis, the synovial membrane thickens and grows more blood vessels, causing even more bleeding into the joint. This picture shows a knee that is swollen from synovitis.
Signs and symptoms of synovitis
- The joint remains swollen and "spongy" even after treatment.
- There is usually no pain or loss of motion unless there is an active bleed.
- There is an increased number of bleeds in the same joint.
Treatment for synovitis
If a joint bleeds more than three times in one month, or if you have any of the symptoms listed above, call your HTC. The medical team will start a treatment plan that may include one or more of these:
- Prophylactic treatment with factor or non-factor therapies. Regular prophylactic treatment will help prevent further bleeding. This will give the synovial membrane a chance to return to normal.
- Oral steroids. These are drugs that reduce inflammation. They are a short-term treatment to be used for only a week or two. Steroids are not used often because they can cause other problems in your body.
- Physical therapy (PT). This can reduce your pain, strengthen your joint and muscles, and prevent loss of motion in the joint.
- Arthroscopic synovectomy. In this surgery, the inflamed part of the synovial membrane is removed. This will not improve your range of motion but can reduce further bleeding and joint destruction.
- Radionuclide synovectomy. A radioactive substance is injected into the joint. The low-level radiation melts away the inflamed synovium.
Ways to prevent synovitis
- Call your HTC if you keep having bleeds in the same joint.
- Stay active and keep your muscles healthy and strong.
- Treat joint bleeds quickly.
- Visit your HTC regularly and have check-ups by the orthopedist (joint doctor).
